
Current Projects
Trial of Intradialytic Cycling as Kidney Exercise Rehabilitation for Cardiac Stunning in Hemodialysis
Dr. Clara Bohm from Winnipeg is leading a randomized control trial with GREX collaborators, to look at the effect of cycling during hemodialysis on heart stunning over a longer time and see whether decreases in heart stunning with exercise improve the fatigue that many people experience after dialysis, symptom burden (the number and severity of symptoms) and other outcomes over 3 months.
This study will be conducted across 7 hemodialysis centres in Canada, the US and Australia.
Identifying Common Physical Function Outcomes
Dr. Jennifer MacRae from Calgary is leading a systematic review with GREX collaborators, to identify the most common outcomes used in trials of exercise and physical activity in patients across the CKD spectrum. The over-arching goal of the project is to provide researchers with a comprehensive list of recommended physical function outcomes to use in future studies.
Cognition and Physical Activity in Chronic Kidney Disease
A group of international GREX researchers are using data from large, population-based databases to better understand the relationship between cognition, physical activity, and CKD both cross-sectionally, and longitudinally. They are also engaging a variety of stakeholders through an international Delphi Survey to identify perspectives on relevant research priorities on cognition in CKD.
Completed Projects
Peritoneal Dialysis Physical Activity and Exercise Recommendations
Led by Paul Bennett, a multidisciplinary group of GREX members are working together to develop clinical best practice recommendations for physical activity and exercise in Peritoneal Dialysis that would also address common clinical PD exercise controversies. The project is being conducted in collaboration with the Standards and Guidelines Committee of the International Society of Peritoneal Dialysis, with the aim of publishing the guidelines, along with producing a series of knowledge translation materials highlighting how clinicians and patients can put the recommendations into action.
The initiative also includes the development and distribution of two global surveys, the first assessing practitioners’ perspectives on exercise and physical activity in PD, which is being led by Mike West (USA), and the second assessing patients’ perspectives, being led by Jennifer MacRae (Canada). A PD exercise guidelines scoping review is also being conducted, led by Kelly Lambert (Australia).
Physical Activity and Exercise Recommendations for People Receiving Dialysis: A Scoping Review
Remaining physically active is important to patients undertaking dialysis, however, clinical recommendations regarding exercise type, timing, intensity, and safety precautions vary. The purpose of this scoping review was to analyse and summarise recommendations for physical activity and exercise for people undertaking dialysis and identify areas that require further research or clarification. The results were published in Public Library of Science: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0267290
Thai PD Recommendations
Somkanya Tungsanga, M.D. Peritoneal Dialysis Excellence Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, BKK, Thailand

Policy Barriers and Enablers to Exercise and Physical Activity

An English pdf of the image above can be found here.
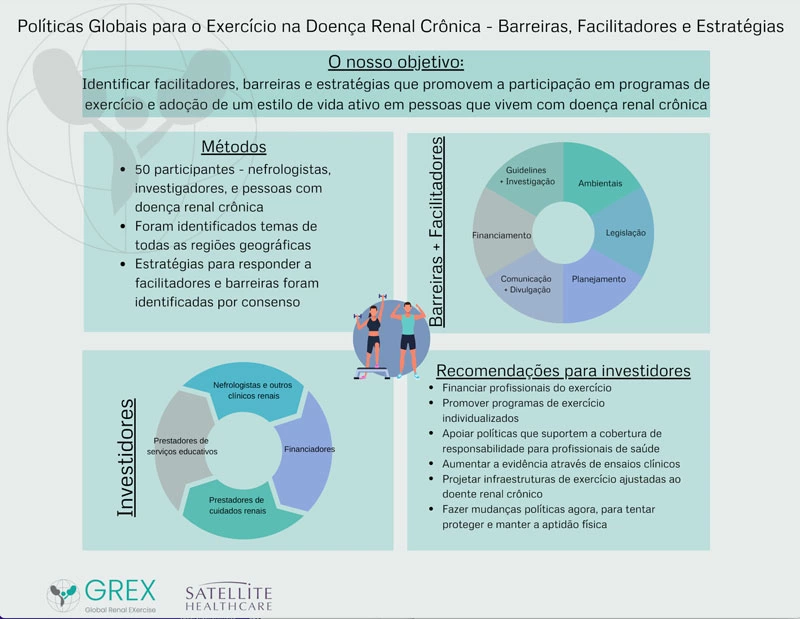
A Portuguese pdf of the image above can be found here.
Physical Activity and Exercise in Peritoneal Dialysis
Life participation requiring physical activity and physical function is a key patient-reported outcome for people receiving peritoneal dialysis (PD). A set of questions relevant to physical activity and exercise were developed
from the perspective of a person receiving PD and were the basis for the practice point development. The results were published in Peritoneal Dialysis International: https://doi.org/10.1177/08968608211055290 and in French: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/suppl/10.1177/08968608211055290
Policy Barriers and Enablers to Exercise and Physical Activity
At the GREX inaugural summit in Calgary in 2019, attendees explored global policy barriers and enablers to exercise and physical activity program implementation in the kidney care space. Guided by the COM-B framework, the group explored fiscal, guideline, environmental, communication, legislation/regulation and service provision barriers and enablers. Fifty contributors from the GREX network (coordinated by Paul Bennett) participated. The results were synthesized in order to provide the first ever global perspective on policy-related exercise barriers and enablers in CKD and ESKD, and were published in the Journal of Renal Nutrition: https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2021.06.007
An International Delphi Survey on Exercise Priorities in Chronic Kidney Disease
Defining the role of exercise in Chronic Kidney Disease is a top research priority for people with CKD. We aimed to achieve consensus on specific research priorities in exercise and CKD among an international panel of stakeholders, including people living with CKD, caregivers, clinicians, researchers, and healthcare administrators. The results were published in Kidney International Reports: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ekir.2020.12.001
